Effect of hydrocortisone on mortality in patients with severe community-acquired pneumonia
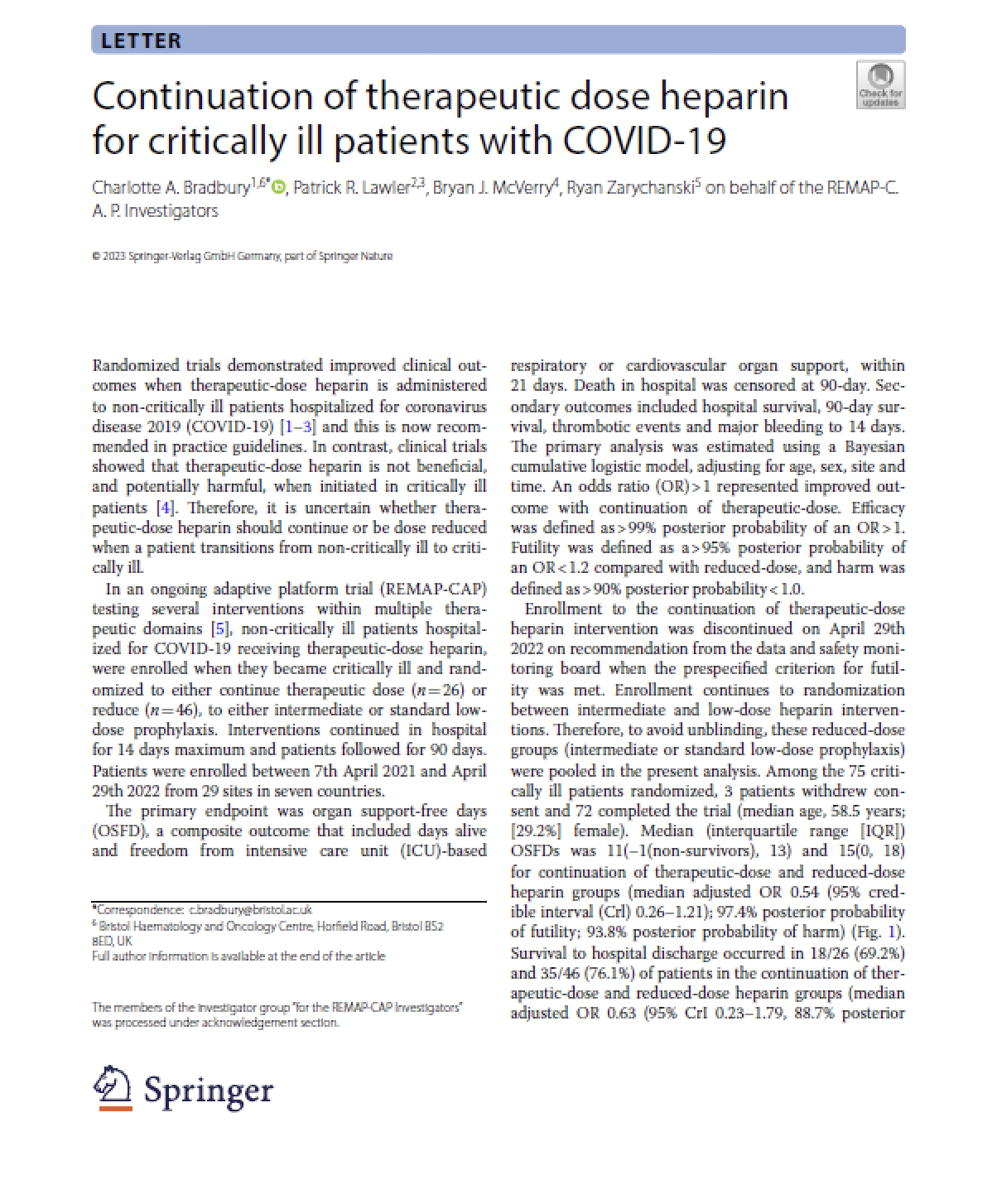
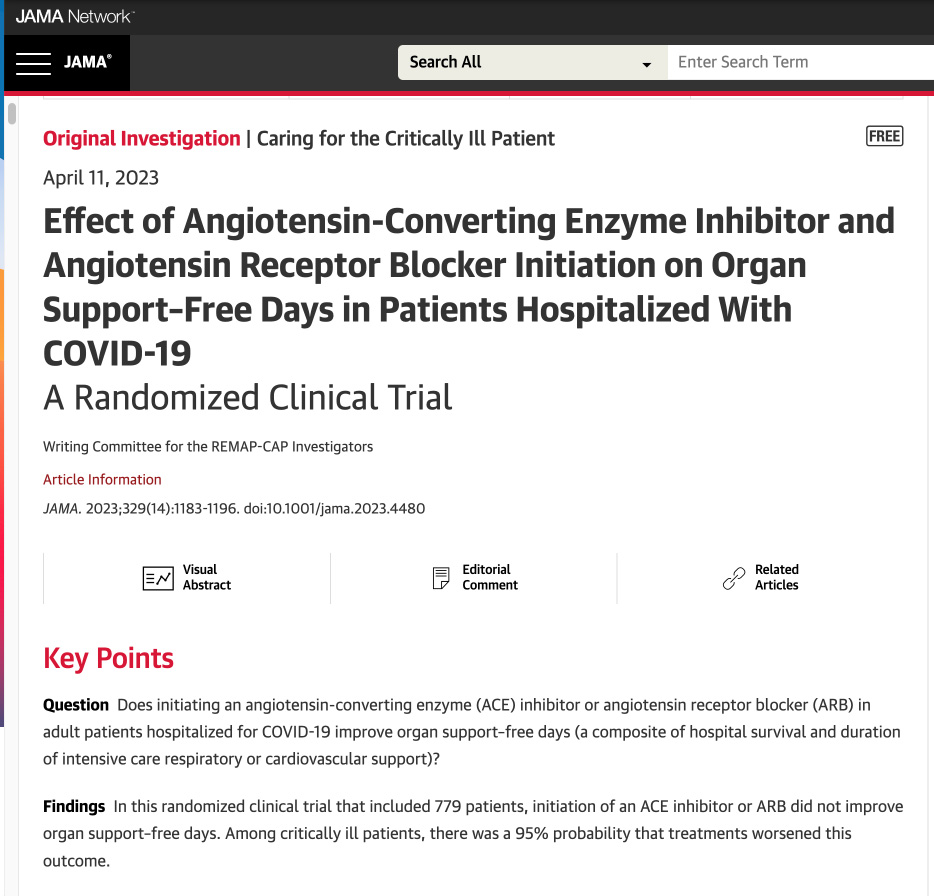
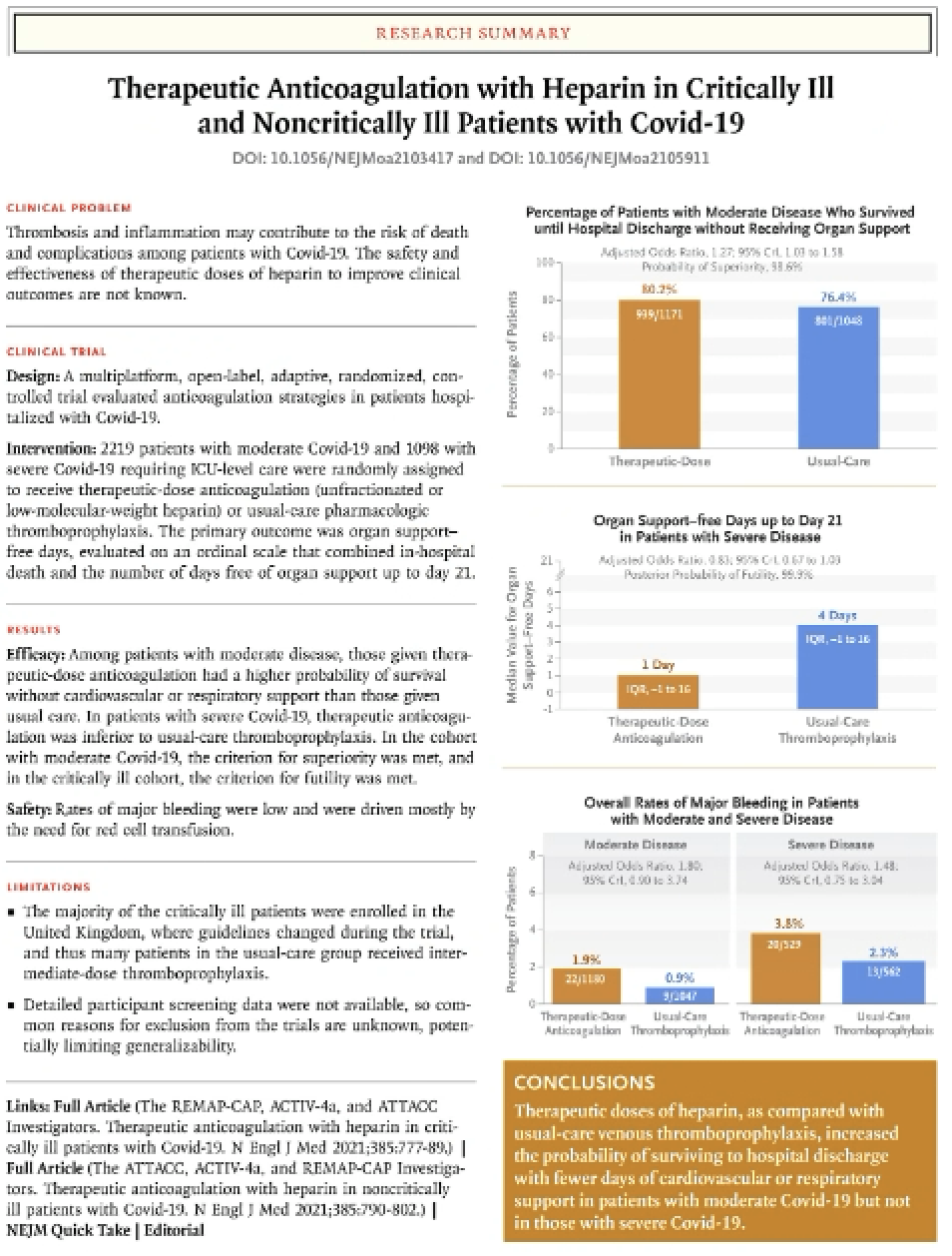
In the REMAP-CAP trial, adults admitted to the intensive care unit (ICU) with severe CAP were randomized to a 7-day course of intravenous hydrocortisone (50 mg every 6 h) or control (no corticosteroid). The primary end point was 90-day all-cause mortality, analyzed iteratively by a Bayesian hierarchical model estimating distinct treatment effects for patients presenting with influenza and shock. Among patients with severe CAP, treatment with a 7-day course of hydrocortisone, compared with no hydrocortisone, appears unlikely to yield a large reduction in mortality. Smaller benefits and possible harm are not excluded.