Simvastatin in Critically Ill Patients with Covid-19
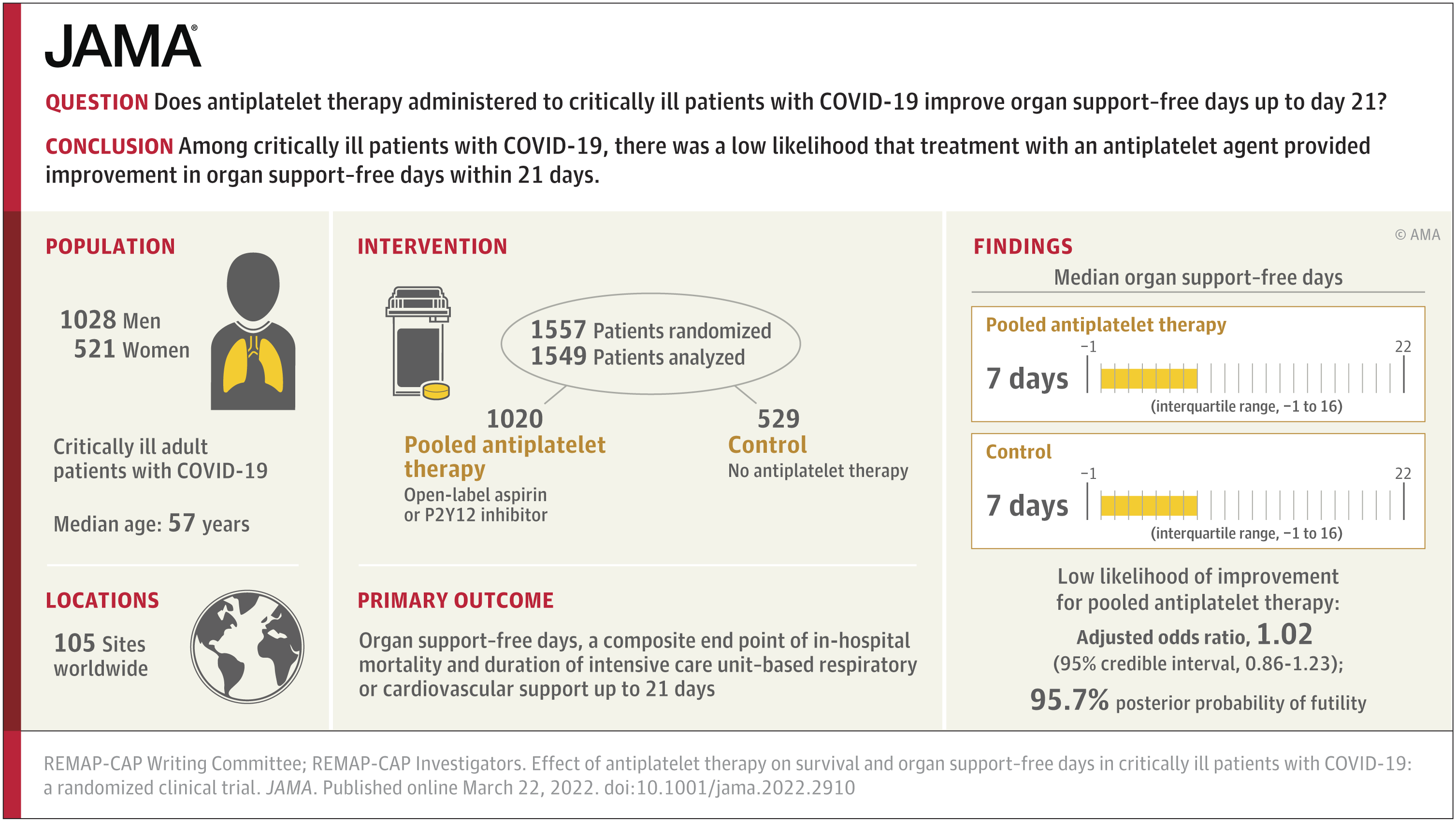
Simvastatin, a widely available and inexpensive drug that is included on the WHO list of essential medicines, was shown to have a high probability (96%) of improving outcomes (a combination of survival and length of time patients need support in an intensive care unit) when started as a treatment for critically ill patients with COVID-19, and a 92% chance of improving survival at 3 months. This equates to one life saved for every 33 patients treated with simvastatin. 2,684 critically ill patients were included at 141 hospitals across 13 countries.